Overview of major sea routes
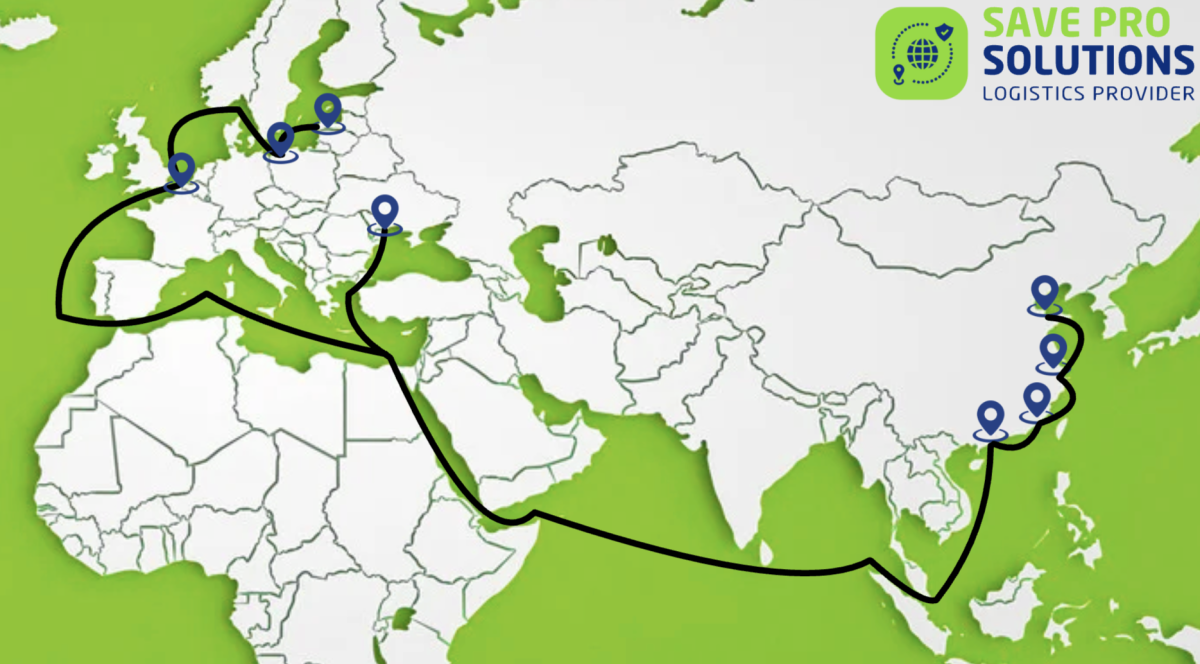
Maritime logistics has been a key element of global trade for centuries. More than 80% of all cargo is transported by sea, as it is the most economical and large-scale method of long-distance transportation. Modern maritime routes connect the world's largest economies, ensuring the movement of goods, raw materials, and energy resources between continents.
For businesses operating in international markets, knowledge of the characteristics of major sea routes helps to optimize deliveries and reduce costs.
Save Pro Solutions organizes international sea freight and helps clients choose the best logistics solutions based on the route, timing, and characteristics of the cargo.
The Suez Canal is a vital transport artery between Europe and Asia
The Suez Canal, located in Egypt, connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea. This engineering masterpiece has significantly reduced the time of sea voyages between Europe and Asia, eliminating the need for ships to circumnavigate Africa via the Cape of Good Hope.
Every day, up to 12% of global maritime traffic passes through the Suez Canal. Oil, gas, cargo containers, machinery, and agricultural products are transported here. Even short-term disruptions in the canal's operation can cause fluctuations in global oil prices and increase freight costs.
The canal is of strategic importance to logistics companies: it provides the shortest connection between Europe, the Indian Ocean, and Asian countries.
The Panama Canal — the key to trade between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans
The Panama Canal, which runs through Panama, connects the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Its opening in 1914 was one of the most significant events in the history of shipping. Thanks to the canal, ships save thousands of kilometers of travel by avoiding the detour around South America via Cape Horn.
After its expansion, the modern Panama Canal is capable of accommodating New Panamax class ships, which can hold up to 14,000 containers. It plays an important role in trade between Asia, the US, and Latin America.
For Ukrainian companies, this route is important in the context of supplying raw materials and equipment, as well as exporting agricultural products to world markets through European ports.
The Strait of Malacca — the trade axis of East Asia
The Strait of Malacca, separating Malaysia and Indonesia, is one of the busiest sea lanes in the world. Up to 25% of all cargo transported by sea passes through it.
The Strait of Malacca connects the Indian Ocean with the South China Sea, ensuring the movement of oil, gas, container and industrial cargo from the Persian Gulf and Southeast Asia. This narrow section is not only a logistical but also a geopolitical center of the region: its security directly affects the stability of the global economy.
The Strait of Hormuz — the planet's energy corridor
The Strait of Hormuz connects the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. Up to 20% of all oil supplied to world markets passes through it every day. Any disruptions in navigation or conflicts in this region instantly affect freight costs and energy prices.
From a logistics perspective, the Strait of Hormuz is an indispensable link for oil tankers, gas carriers, and ships carrying petrochemical products. Therefore, shipping companies carefully plan their routes and schedules depending on the geopolitical situation.
The Strait of Gibraltar — Europe's maritime gateway
The Strait of Gibraltar connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Mediterranean Sea and serves as a natural “gateway” to Europe. This section, only about 60 kilometers long, receives hundreds of ships every day, heading towards the Suez Canal or back to the Atlantic.
More than 100,000 ships pass through Gibraltar each year, from container ships to tankers and refrigerated vessels. The strait is actively used to transport raw materials, fuel, food, and industrial cargo.
It is of indirect importance to Ukraine, as ships carrying cargo to European ports pass through this section, from where they depart for Eastern Europe and Ukraine.
The English Channel (Dover Strait) — a busy route in Northern Europe
The English Channel, or Dover Strait, connects the North Sea with the Atlantic Ocean and separates Great Britain and France. It is one of the most heavily used sea routes on the planet, with up to 500 ships passing through it every day.
Container ships, ferries, tankers, and coastal vessels all cross paths here. The English Channel is a vital artery of European trade and plays a key role in ensuring uninterrupted supplies between the EU countries, the UK, and Scandinavia.
The Bosphorus and Dardanelles — strategic straits of the Black Sea
The Bosphorus Strait, connecting the Black Sea with the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles, leading to the Aegean Sea, are the most important areas for trade in the Black Sea region.
These straits are of particular importance to Ukraine, as they are used to export grain, metals, petroleum products, and chemical cargoes to the Mediterranean Sea and further afield to the rest of the world.
Turkey strictly regulates shipping through the Bosphorus and Dardanelles, making these straits not only logistical but also political objects of strategic importance.
The Danish Strait — the northern gateway to the Baltic
The Danish Straits connect the Baltic and North Seas, providing access for ships from Scandinavia and Eastern Europe to the Atlantic.
Cargo from ports in Poland, Germany, Sweden, Finland, and Denmark passes through it. This route is particularly important for container transport and the transportation of bulk cargo.
For Ukrainian importers, the Danish route is relevant for the delivery of fertilizers, chemical raw materials, feed additives, and industrial equipment.
The St. Lawrence Seaway — North America's transport artery
The St. Lawrence Seaway connects the Great Lakes of North America with the Atlantic Ocean, providing ships with access to the largest industrial centers of Canada and the United States.
It is used to transport grain, coal, steel, cement, chemical products, and industrial cargo.
Although this route is far from Ukraine, it is of interest to logistics operators working with North American partners. It allows for the optimization of routes in multimodal transport, where sea delivery is combined with rail and road logistics.
The Trans-Pacific route — the world's largest trade artery
The Trans-Pacific route connects Asian ports — Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, Busan, Tokyo — with ports on the west coast of the United States and Canada.
It is one of the longest and most important routes, with hundreds of container ships passing through it every day, carrying electronics, cars, textiles, equipment, and raw materials.
With the development of the economies of China and Southeast Asia, the importance of the trans-Pacific route continues to grow. This is where the bulk of the world's container traffic is concentrated.
Key challenges and problems of sea routes
Despite the enormous importance of sea routes, they are subject to a variety of risks. These include geopolitical conflicts, piracy, natural disasters, ship accidents, and water pollution.
Any of these problems can lead to temporary route blockages or increased delivery costs.
Save Pro Solutions closely monitors the international situation and offers customers alternative routes to avoid delays and maintain supply chain stability.
How to choose the optimal sea route
When planning sea delivery, logistics specialists take into account many factors:
- the specifics of the cargo (container, bulk, dangerous, perishable);
- weather conditions and seasonality;
- the state of port infrastructure;
- the level of security;
- the cost of freight and port charges.
Save Pro Solutions offers a personalized approach to route selection: specialists analyze the destination, cargo type, schedule, and customer requirements to offer the optimal solution in terms of timing and budget.
Conclusion
The world's major shipping routes are not just lines on a map. They are vital arteries of the global economy that connect countries, ensure the movement of goods, and shape the stability of international trade.
Understanding the characteristics of each route allows logistics companies to make informed decisions and ensure reliable delivery of cargo to any destination in the world.
Save Pro Solutions helps customers effectively leverage the potential of maritime logistics by combining sea, rail, and road transport to achieve maximum efficiency and security of supply.